The El Nino Affect: Climate Impact on India’s Rice Production and Food Inflation
Jake Hanley, Managing Director | July 13, 2023
![]()
El Nino’s powerful grip on the global economy is tightening, most notably in the rice markets. This crucial commodity, a dietary staple for many, is already feeling the brunt of climate shift. A strengthening and long lasting El Nino could have significant implications for global food markets.
Rising Prices and Export Considerations
Front-month rough rice futures have seen a marked increase of nearly 7% year-to-date, through July 13th, triggered by the current El Nino cycle. Amid rising prices and local inflationary pressures, India, the world's largest rice exporter, is contemplating reducing rice exports. This potential policy change is notable given that India's exports represent roughly 40% of the global rice export market.
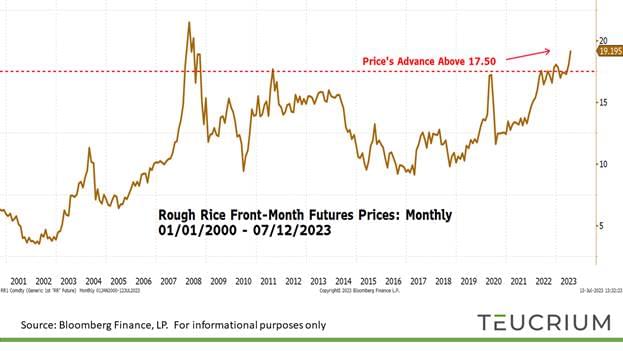
Trade and Grain Demand
China, which relies on imports equivalent to 20% of India's exports to meet its rice needs, may face challenges if India decides to curtail exports. China, along with others, would likely seek alternative markets to mitigate any potential shortfalls. As prices continue to rise, demand might shift towards other commodities. For instance, if rice becomes too expensive or unavailable, consumers could turn to other grains, such as wheat.
The Climate Variable
Weather is the persisting issue here. Drought conditions are already prevalent in key growing regions, and the prognosis isn’t good. The current El Nino is expected to strengthen and extend into 2024. NOAA predicts a 56% chance of severe El Nino conditions developing over the summer and continuing into autumn. This suggests higher-than-normal temperatures and lower rainfall across India's main growing regions for an extended period.
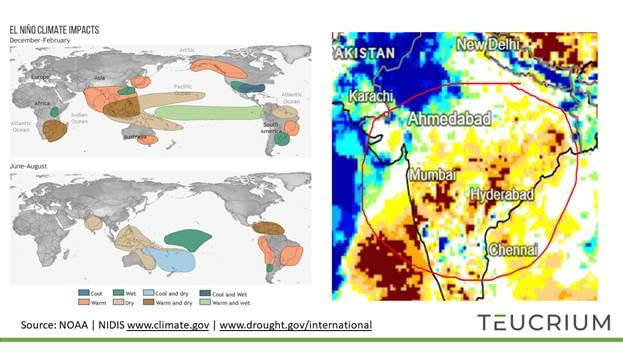
The extent and severity of El Nino are of paramount importance. In terms of growing seasons, India plants 65% of its rice during the Kharif season, starting in May with harvest beginning in September. The remainder of the crop is grown during the Rabi season, with plantings beginning in December and harvest commencing in March. A lingering El Nino poses an increasing risk to the Rabi crop.
Global Food Prices
While food prices have been on a downward trend after reaching unprecedented highs in 2022, the UN Food and Agriculture World Food Price Index is still up over 30% from June 2020 levels. El Nino related production disruptions could potentially add upward pressure on global food prices. Food prices are reflected in headline inflation statistics. As such, central banks around the globe may be facing a set-back in their fight against inflation.

Conclusion
In conclusion, El Nino’s impacts are already being felt throughout the agricultural markets. To the extent that current models prove accurate, we should expect El Nino to strengthen and extend into 2024. This could have a significant impact on India’s rice production, potentially sending ripple effects through global food markets. Stay tuned for our continuing coverage and analysis. Subscribe to our newsletter at www.teucrium.com, and follow us on Twitter @TeucriumETFs.
Disclosure
The information provided is intended to provide a broad overview for discussion purposes. It is subject to change and should not be taken as financial or investment advice. Teucrium Trading LLC and Teucrium Investment Advisors, LLC make no offers to sell, solicitations to buy, or recommendations for any security, nor do they offer advisory services.
Past performance is not indicative of future results. Teucrium disclaims any liability for any actions taken based on the information provided in this document.
